In the realm of data analysis, two roles have emerged as essential components of modern businesses: Business Intelligence Analyst and Data Analyst. While both roles deal with data and insights, they serve distinct purposes and require different skill sets. In this article, we will delve into the differences between these two roles, exploring their responsibilities, required skills, and the value they bring to organizations.
Introduction to Business Intelligence Analyst
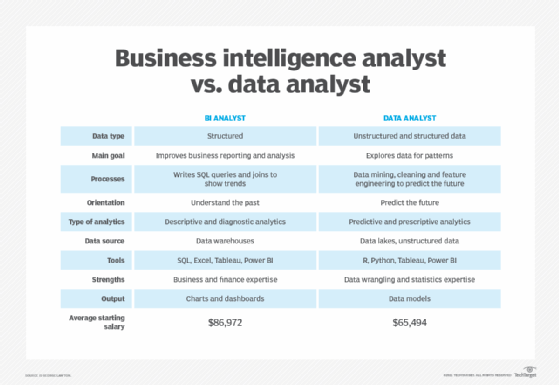
A Business Intelligence (BI) Analyst is responsible for analyzing and interpreting complex data to inform business decisions. They use data visualization tools, statistical models, and machine learning algorithms to identify trends, patterns, and correlations. The primary goal of a BI Analyst is to provide actionable insights that drive business growth, optimization, and innovation. They work closely with stakeholders to understand their needs and develop solutions that address specific business challenges.
Key Responsibilities of a Business Intelligence Analyst:
- Data Analysis: BI Analysts collect, analyze, and interpret large datasets to identify trends, patterns, and correlations.
- Data Visualization: They create interactive dashboards, reports, and visualizations to communicate insights to stakeholders.
- Predictive Modeling: BI Analysts use statistical models and machine learning algorithms to forecast future trends and predict business outcomes.
- Stakeholder Collaboration: They work closely with stakeholders to understand their needs and develop solutions that address specific business challenges.
- Solution Development: BI Analysts design and implement data-driven solutions that drive business growth, optimization, and innovation.
Introduction to Data Analyst
A Data Analyst is responsible for collecting, organizing, and analyzing data to answer specific business questions. They use statistical techniques, data visualization tools, and data manipulation languages to extract insights from datasets. The primary goal of a Data Analyst is to provide accurate and reliable data-driven insights that inform business decisions. They work closely with stakeholders to understand their data needs and develop solutions that address specific business problems.
Key Responsibilities of a Data Analyst:
- Data Collection: Data Analysts collect and organize data from various sources, including databases, spreadsheets, and external data providers.
- Data Analysis: They analyze data to identify trends, patterns, and correlations, and answer specific business questions.
- Data Visualization: Data Analysts create reports, visualizations, and dashboards to communicate insights to stakeholders.
- Data Quality: They ensure data accuracy, completeness, and consistency, and develop processes to maintain data quality.
- Stakeholder Support: Data Analysts provide data-driven insights and support to stakeholders to inform business decisions.
Key Differences between Business Intelligence Analyst and Data Analyst:
- Focus: BI Analysts focus on strategic, high-level analysis, while Data Analysts focus on tactical, operational analysis.
- Scope: BI Analysts have a broader scope, analyzing data from multiple sources to inform business decisions, while Data Analysts have a narrower scope, analyzing specific datasets to answer business questions.
- Skill Set: BI Analysts require advanced analytical, technical, and business skills, while Data Analysts require strong analytical, technical, and communication skills.
- Decision-Making: BI Analysts are involved in strategic decision-making, while Data Analysts provide insights that inform operational decisions.
Required Skills for Business Intelligence Analyst and Data Analyst:
- Analytical Skills: Both roles require strong analytical skills, including data analysis, statistical modeling, and data visualization.
- Technical Skills: BI Analysts require advanced technical skills, including programming languages (e.g., Python, R), data visualization tools (e.g., Tableau, Power BI), and machine learning algorithms. Data Analysts require proficiency in data manipulation languages (e.g., SQL), statistical software (e.g., Excel, SPSS), and data visualization tools.
- Business Acumen: BI Analysts require strong business acumen, including knowledge of industry trends, market analysis, and competitive intelligence. Data Analysts require a basic understanding of business operations and market trends.
- Communication Skills: Both roles require strong communication skills, including the ability to present complex data insights to non-technical stakeholders.
Value to Organizations:
- Informed Decision-Making: Both BI Analysts and Data Analysts provide data-driven insights that inform business decisions, drive growth, and optimize operations.
- Competitive Advantage: BI Analysts help organizations stay ahead of the competition by identifying trends, patterns, and correlations that inform strategic decisions.
- Operational Efficiency: Data Analysts help organizations optimize operations by providing insights that improve processes, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Innovation: BI Analysts drive innovation by identifying new business opportunities, developing predictive models, and creating data-driven solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
- What is the primary difference between a Business Intelligence Analyst and a Data Analyst?
The primary difference is the scope and focus of their work. BI Analysts focus on strategic, high-level analysis, while Data Analysts focus on tactical, operational analysis. - Do I need a degree in computer science or mathematics to become a Business Intelligence Analyst or Data Analyst?
While a degree in computer science or mathematics can be beneficial, it is not necessarily required. Strong analytical, technical, and business skills are essential for both roles. - What tools and technologies do Business Intelligence Analysts and Data Analysts use?
BI Analysts use data visualization tools (e.g., Tableau, Power BI), programming languages (e.g., Python, R), and machine learning algorithms. Data Analysts use data manipulation languages (e.g., SQL), statistical software (e.g., Excel, SPSS), and data visualization tools. - Can I transition from a Data Analyst role to a Business Intelligence Analyst role?
Yes, with additional training and experience, Data Analysts can transition to BI Analyst roles. They will need to develop advanced analytical, technical, and business skills to succeed in this role. - What is the average salary for a Business Intelligence Analyst and a Data Analyst?
The average salary for a BI Analyst is around $80,000 – $110,000 per year, while the average salary for a Data Analyst is around $60,000 – $90,000 per year.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, while both Business Intelligence Analysts and Data Analysts deal with data and insights, they serve distinct purposes and require different skill sets. BI Analysts focus on strategic, high-level analysis, while Data Analysts focus on tactical, operational analysis. Both roles are essential components of modern businesses, providing data-driven insights that inform business decisions, drive growth, and optimize operations. By understanding the differences between these two roles, organizations can better leverage their talents and expertise to achieve their goals. Whether you are an aspiring analyst or an organization looking to hire analytical talent, it is essential to recognize the unique value that each role brings to the table.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Business Intelligence Analyst vs Data Analyst: Understanding the Difference. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!